BLOG: APPLIED RESEARCH OF EMMANUEL GOSPEL CENTER
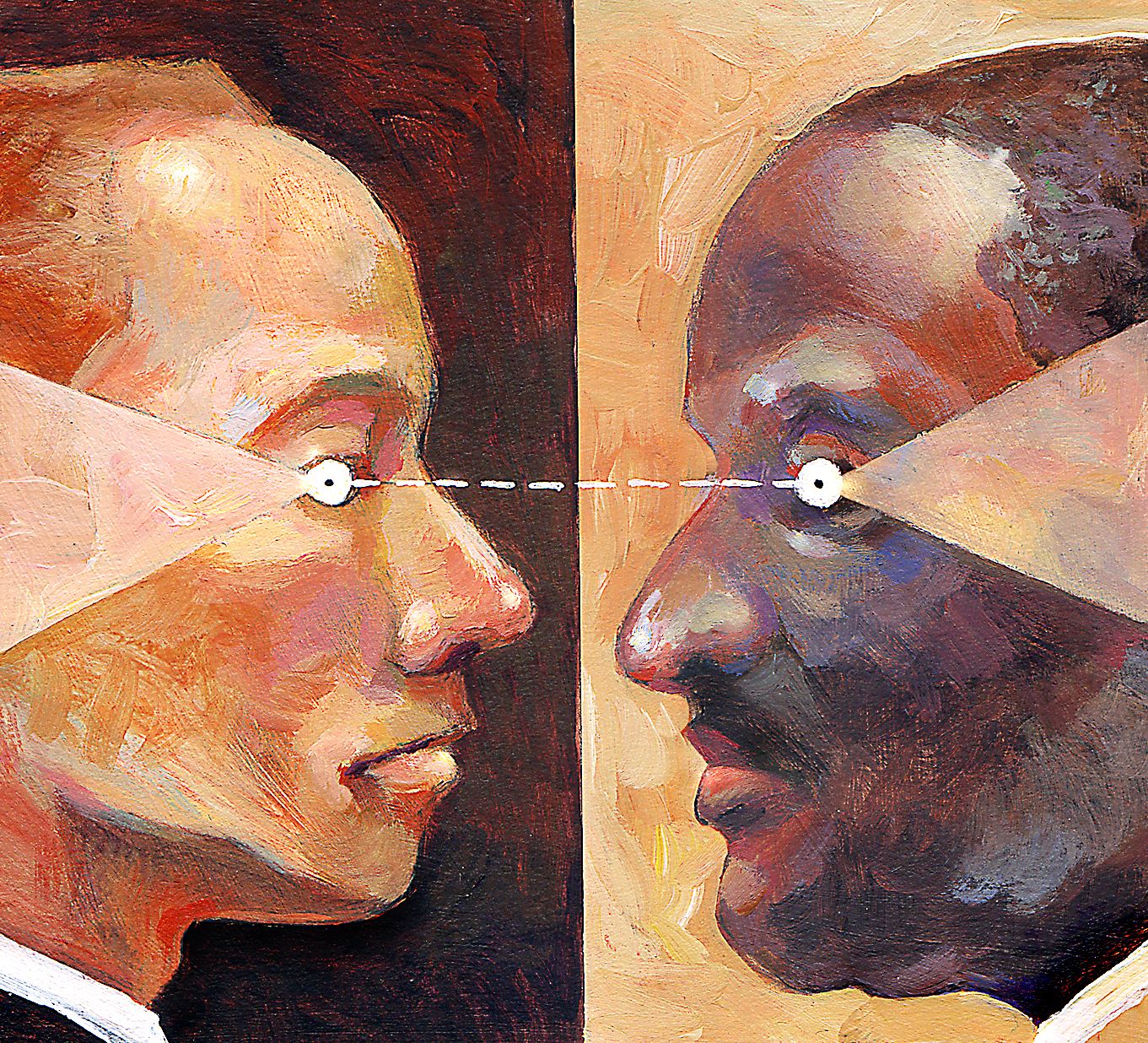
Starter Resources on Race for White Evangelicals
You're White, and you want to engage responsibly and respectfully on race issues. You're an evangelical, and you believe the ministry of reconciliation is part of your calling as a follower of Jesus. Where do you begin? Check out these starter resources recommended by Megan Lietz, a White evangelical committed to helping other White evangelicals on their race journey.
Starter Resources on Race for White Evangelicals
by Megan Lietz
Biblical and Theological Foundations
As with all matters, it’s important that we root our understanding in God’s word. Explore the following resources to better understand the biblical and theological foundation of continuing God’s redemptive work across racial lines.
A Theology of Racial Healing: Though the word “racism” is not used in the Bible, scripture tells the story of God reconciling all people to himself and one another. In this resource, RCCI suggests a Biblically-grounded theology on Christ's redemptive work in the area of race relations.
The Sin of Racism: Though racism is often not named as a sin from the White evangelical pulpit, this article by Tim Keller explains from a biblical perspective how racism is a sin and that it manifests individually and corporately. Though there is disagreement around how to respond to racism, as Christians, we cannot leave this sin unaddressed.
Ethnic Identity: Bringing Your Full Self to God: God gave each one of us ethnic identities that reflect the character and image of God. Explore what the Bible has to say about ethnicity and culture in this self-led Bible study for groups and individuals. It reveals how God sees our ethnic identity and uses it as a part of his redemptive plan.
Race & Racial Hierarchy as the Product of Broken Humanity
While our ethnicities were given to us by God, the social classification of race and the racial hierarchy it serves was a product of a broken humanity. To learn more about how the concept of race developed and was shaped by socio-historical realities, not God’s will, explore the following resources.
Race: The Power of Illusion: This is a three-part PBS documentary that explores the origins of race and how it is not a genetic reality, but a relatively new social construct. Though somewhat dated, the foundation laid here is important to understanding the concept of race. If only one episode is watched, it is recommended to watch Part 2: The Story We Tell. It can be rented on vimeo or is available via Kanopy subscription service, that may be available through a local library.
Our Experience and Identity as White People
In order to engage effectively as white people in issues of race we need to understand how our experiences and perspectives may be different from those of people of color. An important part of this is understanding the racial privilege and power we have as White people because of the color of our skin. For some perspective, check out the following resources.
If you’re looking for a primer on how aspects of our identity like race and gender grant us measures of privilege and how they can impact our lived experience check out Allan Johnson’s book, Privilege, Power, and Difference.
Waking Up White is a memoir by Debby Irving, a white woman who grew up in a predominantly white, wealthy suburb of Boston, about how she came to see and respond to her whiteness. Her journey can offer insights and encouragement for your own.
In, White Awake: An Honest Look at White It Means to Be White, Daniel Hill leads readers through phases of White identity development and offers biblical tools to navigate these seasons of growth. He also offers strong chapters on markers of racial awareness and action steps you can take to progress in your racial awareness journey.
Peggy McIntosh’s article, White Privilege: Unpacking the Invisible Knapsack, is a brief and classic work that gives examples of how white people may experience privilege in their daily life. Simply becoming aware of what privilege looks like and how it can manifest in our lives is a crucial step!
Engaging Issues of Race
As we explore our identity as white people, we need to consider how this shapes our role in engaging issues of race and develop a toolkit for effective action.
Woke Church, by Eric Mason, explores the biblical call to justice that is for all believers and how the Church can regain its prophetic voice and practice to confront racism in the United States.
How to Be Last: A Practical Theology for Privileged People is a blog post by Christena Cleveland that lays a theological foundation for the posture that white people should take as they follow people of color into the work of racial reconciliation.
Soong Chan Rah’s book, Many Colors: Cultural Intelligence for a Changing Church, explores what Christians need to know and do to engage across racial lines in ways that are loving and respectful.
Mark Kramer’s article, Unpacking White Privilege: Feeling Guilty about Racial Injustice Isn’t the Point; the Point Is Doing Something About It complements Peggy’s McIntosh’s article by offering suggestions for how to respond to some of the privileges she identifies.
For additional resources, check out Next Step Resources for White Evangelicals.
Take ACTION
Megan Lietz, M.Div., STM, helps White evangelicals engage respectfully and responsible with issues of race. She is the director of EGC’s Race & Christian Community Initiative.
Urban Youth Culture Research [Resource List]
How are people of faith to understand urban youth culture? How can the Church best interact with urban youth? Youth and Culture Professor Dean Borgman provides qualitative research resources for the urban youth practitioner to develop a framework and approach for more effective ministry.
Urban Youth Culture Research [Resource List]
by Rev. Dean Borgman, Professor of Youth Ministry
How are people of faith to understand urban youth culture? How can the Church best interact with urban youth?
This post provides qualitative research resources for the urban youth practitioner to develop a framework and approach for more effective ministry.
Current Resources
“Barking to the Choir: The Power of Radical Kinship,” by Gregory Boyle (2017)
Though not social science, Barking to the Choir offers what I call “qualitative research snapshots”. This spiritual and biblical reflection on the lives of L.A. homies illustrates what is required for effective qualitative research: time spent and trust felt. Urban researchers will see possible results of their work, as this book describes how homies from negative origins can transform into effective workers and young entrepreneurs.
“Tattoos on the Heart: The Power of Boundless Compassion,” by Gregory Boyle (2010)
Though Father Boyle is not a social science researcher, what this white, adult, professional (a priest) displays in the way relationships can provide the most "human" kind of information, and serve as a passage from gang-ridden neighborhoods to positive community development (a thriving bakery business). This book is about a God who shows up in surprising ways and places with unconditional compassion, sense of humor, strength and firmness.
This site includes description of “Community-Based Participatory Research,” “Research, Action, Activism: Urban Gathers for Third National Meeting: ‘critical solidarities and multi-scalar powers,’” and “From Youth Organizers to Social Justice Activists' Experiences of Youth Organizers Transitioning to Adulthood.”
Emmanuel Gospel Center, Boston
EGC has engaged in urban applied research in collaboration with other agencies for decades.
Resources on Economic Systems
Without understanding economic realities surrounding urban youth, we do not have a complete picture of what drives youth culture. Employment challenges and informal/underground economic systems are two of these realities. For a recent study of global informal underground economic systems, see Edgar L. Feige and Paulina Restrepo-Echavarria.
“Defining and Estimating Underground and Informal Economies: The New Institutional Approach,” by Edgar L. Feige (10 Jun 16)
“Measuring Underground Economy Can Be Done, but It Is Difficult,” by Paulina Restrepo-Echavarria (Jan 2015)
Classic Resources
Article: “The Code of the Streets,” by Elijah Anderson (May 1994), The Atlantic
Understanding the influences, behaviors, and motives of urban communities and their youth has been greatly furthered by the work of African-American sociologist Elijah Anderson, Professor at the University of Pennsylvania (and now Yale). Anderson’s work is must-reading for urban street workers and should be understood by all serving urban neighborhoods. It is worth quoting from this insightful article:
“Of all the problems besetting the poor inner-city black community, none is more pressing than that of interpersonal violence and aggression…. The inclination to violence springs from the circumstances of life among the ghetto poor—the lack of jobs that pay a living wage, the stigma of race, the fallout from rampant drug use and drug trafficking, and the resulting alienation and a general lack of hope for the future.”
Code of the Street: Decency, Violence, and the Moral Life of the Inner City by Elijah Anderson (1999)
Anderson’s book further builds on his 1994 article and describes the details of the code of the streets that so strongly influences inner-city life. Inner-city youth come out of their apartments to “Win-Win/Lose-Lose” street situations… as part of a “zero-sum game.” They are forced into a “campaign for self-respect,” where “juice” (or power over others) are crucial. Code of the Street details the bigger picture—the systemic context for what average citizens see as a stereotype of urban lives from the evening news.
Streetwise: Race, Class and Social Change in an Urban Community by Elijah Anderson (1990)
Anderson’s earlier book, Streetwise, is a careful analysis of social neglect and intrusion (gentrification) in urban life.
Street Corner Society: The Social Structure of an Italian Slum by William Foote Whyte (1993)
Back in the late 1930s William F. Whyte, on a fellowship from Harvard, lived in Boston’s North End. As an early social scientist he attempted to describe life in that Italian-American community of first-and second-generation immigrants. First published in 1943, it was entitled Street Corner Society: The Social Structure of an Italian Slum. Whyte’s work is important to us as it pioneered what he described as “participant observer research,” and provides a foundation for systems thinking ministry.
Street Corner Research: An Experimental Approach to the Juvenile Delinquent by Ralph K. Schwitzgebel (1993)
Also coming out of Harvard and influenced by the work of William Whyte is Ralph Schweitzgebel’s Streetcorner Research: An Experimental Approach to the Juvenile Delinquent. Its considerations of qualitative research emphasizes the importance of genuine relationships for urban study of youth, and describes delinquency as having a variety of psychological and sociological causes.
Ain’t No Makin’ It: Aspirations & Attainment in a Low-Income Neighborhood by Jay MacLeod (1995)
Any urban program using interns, and certainly urban interns themselves, should be interested in the story of three students wandering into an urban housing project seeking to set up a youth program.
Working with youngsters in a poor neighborhood for several summers, the author decided to write his undergraduate thesis on the occupational aspirations of two contrasting cliques of older teenagers in the project—the Hallway Hangers and the Brothers: “I immersed myself in their peer cultures for a year and tried to understand the two groups from the inside. Exploring their aspirations led me into a thicket of enduring social issues about the nature of poverty, opportunity, and achievements in the United States.” MacLeod’s book continues to be a classic sociology text.
In Search of Respect: Selling Crack in El Barrio by Philippe Bourgois (1995)
A study emphasizing the importance of urban economics is Philippe Bourgois’ “In Search of Respect: Selling Crack in El Barrio”. This anthropologist and urban researcher moved into Spanish Harlem, NYC, and established long-term friendship and trust with Puerto Rican, street-level drug dealers... spending many a night in crack havens. “I was interested in the political economy of inner-city street culture…. I wanted to probe the Achilles heel of the richest industrialized nation in the world by documenting how it imposes racial segregation and economic marginalization on so many of its Latino/a and African-American citizens.”
Our America: Life and Death on the South Side of Chicago, by LeAlan Jones and Lloyd Newman with David Isay (1997)
Community programs hoping to use youthful residents for urban research can learn from Jones and Newman, two young teenagers who retrieve a story about the incomprehensible dropping of a five-year-old boy from a 14th floor window by 10-and 11-year old kids because he wouldn’t steal candy for them. With transistor recorders and some coaching from Isay, these teens collected what can be considered informal, qualitative research for two years—when they were thirteen and fourteen years old. Reading their report allows for a better understanding of inner-city values and attitudes.
“Constructing Meaning About Violence, School, and Community: Participatory Action Research with Urban Youth,” by Alice McIntyre (2000), The Urban Review, Vol.32, No.2, 2000.
A scholarly article describing how a group of adolescents were equipped to study and report on “a toxic environment, limited social services, poverty, crime, drugs, and inadequate educational resources.”
Final Note: Most of the above suggest going beyond relief and incarceration and even prevention to community development. But few go as far as to suggest what needs to be changed in the realm of what might be called systemic injustice, which includes racism and classism.
2018 Resources for Urban Youth Workers on Cultural Trends
How can busy youth workers and ministers stay on top of trends affecting youth? Dean Borgman offers some starting points.
2018 Resources for Urban Youth Workers on Cultural Trends
by Rev. Dean Borgman, Professor of Youth Ministry
While nothing can substitute for personal relationships of understanding and trust with youth, we also need to get a grip on the bigger picture. We need to see beyond our kids, family, church, and community—to what’s going on in the society and culture. These resources provide a wide angle lens on what our kids step into when they leave the house.
BEST GENERAL RESOURCES
Watch the watchers. Way back in 1980, I found out that the people who know the most about youth in this country are not the youth ministry professors (of which I am one), but the marketers.
So I’ve been following the marketers and what they find out about young people. YPulse is one of the marketing sources I regularly visit. They regularly update information on trends in youth culture.
Two scholars I’ve looked to for information especially in the last few years on trends in youth culture are MIT's Sherry Turkle and San Diego State University's Jean Twenge.
Jean Twenge uses four major youth studies that come out every year from the government and universities, so her research is based on a sampling of 11 million teenagers—ample data to back up her conclusions.
Finally, the Barna Group, a broadly reputable Christian organization, does generational research.
SPECIAL FOCUS
If we're talking about youth in 2018, we're already talking about Black Panther and activism against gun violence. But two other issues deserve our special focus this year. These are depression and cell phone use.
DEPRESSION
CELL PHONE USE
Join the Conversation: Honor-Shame Culture in US Cities & Churches
The dynamics of shaming affect your church community more than you might think. Guest contributor Sang-il Kim raises awareness for Boston Christian leaders to a surprising level of honor-shame dynamics in US urban culture. Join the conversation!
Join the Conversation: Honor-Shame Culture in US Cities & Churches
By Jess Mason, Supervising Editor
Before I had the pleasure of meeting Sang-il Kim, a Ph.D. candidate at BU School of Theology, I thought honor-shame dynamics were limited to specific cultures of the Far East, Middle East, and Africa. I was wrong.
My limited personal experience with honor-shame culture comes from my brief journey to China with a team of pastors. There I witnessed our cross-cultural guide go to an ATM, withdraw a wad of cash, and present it to our Chinese host, after we had unknowingly offended our Chinese friends in some way. She had received our shame and made the culturally appropriate gesture to restore our honor in their eyes.
Last month, Mr. Kim opened my eyes to the surprising levels of honor-shame dynamics now present in US cities, including Boston. Notably, he said that the American face of honor-shame dynamics today goes far beyond immigrants from traditionally honor-shame cultures.
I was inspired to brainstorm with him what it could mean for Boston area pastors—what does it look like to shepherd well amidst this emerging dynamic of honor and shame?
Mr. Kim's full article (below) aims to raise the awareness of Boston Christian leaders to honor-shame culture in their congregations, communities, and theology. EGC invites you to join him for conversation, and consider with others how you might engage honor-shame dynamics to the glory of God.
Sang-il Kim is a doctoral candidate in Practical Theology and Religious Education at Boston University. His dissertation delves into the harmful effects of shame and how teaching and learning Christian doctrines can be an antidote to them. Sang-il plans to balance teaching and research on human emotion and Christian theology, with youth and adult Christian formation in view.
Keywords
- #ChurchToo
- 365 Campaign
- ARC Highlights
- ARC Services
- AbNet
- Abolition Network
- Action Guides
- Administration
- Adoption
- Aggressive Procedures
- Andrew Tsou
- Annual Report
- Anti-Gun
- Anti-racism education
- Applied Research
- Applied Research and Consulting
- Ayn DuVoisin
- Balance
- Battered Women
- Berlin
- Bianca Duemling
- Bias
- Biblical Leadership
- Biblical leadership
- Black Church
- Black Church Vitality Project
- Book Recommendations
- Book Reviews
- Book reviews
- Books
- Boston
- Boston 2030
- Boston Church Directory
- Boston Churches
- Boston Education Collaborative
- Boston General
- Boston Globe
- Boston History
- Boston Islamic Center
- Boston Neighborhoods
- Boston Public Schools
- Boston-Berlin
- Brainstorming
- Brazil
- Brazilian
- COVID-19
- CUME
- Cambodian
- Cambodian Church
- Cambridge























![Urban Youth Culture Research [Resource List]](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/57ff1c7ae58c62d6f84ba841/1530294363902-G2R6K4YMB3AX42HOIMH9/black-and-white-crowd-gang-38198.jpg)







































![Beyond Church Walls: What Christian Leaders Can Learn from Movement Chaplains [Interview]](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/57ff1c7ae58c62d6f84ba841/1550010291251-EVMN3KQ15A70OBTAD4JQ/movement-chaplaincy_outdoorcitygroup.jpg)









