Perspectives on Boston Church Statistics: Is Greater Boston Really Only 2% Evangelical?
Resources for the urban pastor and community leader published by Emmanuel Gospel Center, Boston
Emmanuel Research Review reprint
Issue No. 88 — April 2013
Introduced by Brian Corcoran, Managing Editor, Emmanuel Research Review
What are the sources, accuracy, limitations, and weaknesses of some commonly used church statistics, especially with regard to their application in Boston? Wanting to encourage a more appropriate use of church statistics generally and in Boston, Rudy Mitchell, Senior Researcher at EGC, considers some of the more popular sources we encounter on the internet or in the news media, such as:
The U. S. Religious Census and the Association of Religious Data Archives
The Barna Research Group, and
Gallup Polls on Religion.
Rudy offers some quick and practical advice for those who are tempted to grab-and-go with the numbers, as if they were “gospel” to their next sermon, strategic planning meeting, church planting support fundraising website, or denominational report. As convenient and convincing as statistics are, beware! They also can be easily misunderstood, misapplied, and generate misinformation.
True or false?
“...only 2.1% of the people living in greater Boston attend evangelical churches.”
“Tragically, only 2.5% of the 5.8 million people in greater Boston attend an evangelical church.”
“Boston is...97.5% non-evangelical.”
“There are fewer than 12 Biblical, Gospel Centered, Soul-Winning Churches” among the “7.6 million people” in Greater Boston.
The twitter-speed circulation of misinformation about Greater Boston being only 2% evangelical contributes to an inaccurate portrayal of what God has been doing in Greater Boston for decades by failing to recognize the ministry of many existing evangelical churches. Furthermore, it misdirects the development of new ministries and leaders emerging and arriving in Boston each month.
The good news is that the local church research conducted by the Emmanuel Gospel Center in Boston over the last 40 years has identified a larger, more vital, and more ethnically diverse Church than suggested by recent and broader church research projects. With the benefit of a comprehensive database and directory of the churches in Boston, developed over decades, EGC has the opportunity to compare and contrast our street-by-street Boston results with broader, less dense, bird’s-eye-view national research. With all this info in hand, we can illustrate how Boston’s evangelical churches have been significantly underreported in national surveys and suggest that they might also be underreported in some other major U.S. cities. Go ye therefore and research your city.
Furthermore, given the longevity of our research, we have been able to identify what we call Boston’s “Quiet Revival,” which is characterized by growth in the number of churches and church attendees, increased collaborative ministry, and multiple interrelated prayer movements in Boston since 1965. Currently there are approximately 700 Christian churches in the three cities of Boston, Brookline and Cambridge in the heart of Metro Boston, and these churches include folks from many tongues, tribes, and nations.
God is and has been doing more in Boston than most national survey techniques can identify.
Perspectives on Boston Church Statistics: Is Greater Boston Really Only 2% Evangelical?
by Rudy Mitchell, Senior Researcher, Emmanuel Gospel Center
Infographics by Jonathan Parker
What about the U. S. Religious Census and the Association of Religious Data Archives (ARDA)?
The 2010 U.S. Religious Census was collected by the Association of Statisticians of American Religious Bodies (ASARB) and also presented by the Association of Religion Data Archives (ARDA). The 2010 U.S. Religious Census provides data by county and by metropolitan area. The method used by this census is basically to compile the numbers of churches and adherents, denomination by denomination. The Boston city data is a part of Suffolk County, which also includes the cities of Chelsea, Winthrop and Revere.
Through our research at Emmanuel Gospel Center, we have identified over 500 Christian churches within the city limits of Boston. The other three cities in Suffolk County have at least an additional 54 churches. Therefore, through first-hand research, we have counted at least 554 Christian churches in Suffolk County. The U.S. Religious Census counted only 377 Christian churches.1 Thus their count misses at least 177 churches. Because many new churches have been planted since our last count in 2010, we estimate that the U.S. Religious Census may have missed as many as 200 to 240 churches. In urban areas, the U.S. Religious Census / ARDA statistics are especially inaccurate because few African American, Hispanic, and other immigrant churches are counted, since many do not appear in the denomination lists used by the census. Other independent churches, some of which are very large, are often missed as well.
While the U.S. Religious Census perhaps needed to make some simple classifications of churches for the national compilations, these classifications are oversimplified and often misleading, especially at the local level. In urban areas there are many evangelical churches within denominations classified as “Mainline.” For example, in the city of Boston, the vast majority of American Baptist Churches (classified as Mainline) are evangelical. Other so-called “Mainline” denominations have some evangelical churches in Boston as well. Therefore, if one compiles the number of evangelical churches and adherents only from the list of churches classified as “Evangelical” by the U.S. Religious Census, one will end up with serious errors.
In addition, while the term “evangelical” is not typically used by African American churches, a majority of those churches would be considered “evangelical” in light of their beliefs and practices. This is also true of most Protestant Spanish-speaking and Haitian churches. In Suffolk County our research has identified at least 120 Spanish-speaking churches, and the vast majority of these are evangelical. Therefore, counts of evangelical churches and adherents must include these and additional immigrant evangelical church groups, if they are to be accurate.
Likewise, in urban areas like the city of Boston, most Black Protestant churches are missed by the U.S. Religious Census. The commentary notes that this is the case. Although the census attempted to include the eight largest historically African American denominations, it fell far short of gathering accurate numbers for even these denominations. “Based on the reported membership sizes included in the address lists, less than 50% of any group’s churches or members were able to be identified… For the African Methodist Episcopal Church, they found approximately the correct number of congregations, though the membership figures are only about one-third of their official reports. For other groups, the church counts range from 11% to 50% of reported numbers, and membership figures are from 7% to 28% of the reported amounts.”2 In the case of Boston, one can see just how far off these numbers are. The Boston Church Directory research identifies 144 primarily African American churches, 19 Caribbean/West Indian churches, 9 African churches, and 34 Haitian churches in the city of Boston for a total of 206 Black churches. In contrast, the U.S. Religious Census identifies only 23 Black Protestant churches in all of Suffolk County. Thus the Census identifies (as Black Protestant) less than 11% of the Black churches that exist in the city. Given the size and importance of Black churches in urban areas, the U.S. Religious Census is completely inadequate in assessing religious participation in cities. Many of these churches belong to small denominations or are independent. While some Black churches are counted as part of evangelical and mainline denominations, they are not identified as Black churches.
At a time when hundreds of new evangelical churches have been planted in Boston and the greater Boston area, a number of church planters and media sources continue to lament the “cold, dark, sad and tragic” state of the Boston spiritual climate. While there is still a need for increased growth and vitality of many current churches, and a need for new church plants, these reports often give a one-sided and overly pessimistic view of the state of the Christian church in Boston. It is common to hear that only 2.1 or 2.5% of greater Boston residents are evangelicals. This number is passed on from source to source without question, often morphing and attaching itself to various subgroups of the population. This percentage underestimates and diminishes the work of God which is going on in greater Boston.
One can easily glean a sad harvest of bad news about Boston on the internet. For example, a web-posted Boston church planting prospectus says, “What most people do not consider is the spiritual brokenness that fractures the city. They fail to realize that the spiritual climate is incalculably colder than the lowest lows of a Boston winter…most remain blind to the spiritual darkness that pervades the city. Tragically, only 2.5% of the 5.8 million people in greater Boston attend an evangelical church. Not surprisingly, there are very few healthy evangelical churches…” Another church planter said, “According to one very thorough study, only 2.1% of the people living in greater Boston attend evangelical churches.” One church planter recalled God’s call, “God said, “I’m going to give you somewhere.’ I had no idea he was going to give me one of the hardest cities in the United States to go plant a church in…Boston is very intimidating. It’s 97.5% non-evangelical. For those non-math people, that’s 2.5 percent evangelical Christian. I didn’t even know there was a city like that before I started studying it.” While it may be more difficult to plant a new church in urban Boston than in suburban Texas or North Carolina, hundreds of successful churches have been planted in greater Boston in the last few decades.
In the city of Boston and surrounding towns, God has raised up new churches among many different groups of people. For example, in the city of Boston alone, more than 100 Spanish language churches have been planted. Many of these are not counted in typical “thorough” studies because they are either independent or do not belong to the denominations counted in these studies. In greater Boston there are even more Spanish speaking churches than in the city itself. Likewise the research often referenced does not count most of the Brazilian churches in greater Boston. The majority of the 420 Brazilian churches in eastern New England are located in Greater Boston. As many as 180 of these churches are nondenominational or directly affiliated with their denominations in Brazil, and therefore not counted in the ARDA data.3 Scores of African American, Haitian, African, Korean, Indonesian, and Chinese churches have also been planted in this area as well. Most, if not all of these immigrant churches would be considered evangelical. While some of these are small, quite a number of the churches have hundreds of active participants. Although one church planter claimed there was only one successful Anglo church plant, a little more research would have revealed that God has been growing many new and successful churches among this group, especially reaching Boston’s young adult population.
The source for some of the above statistics on greater Boston is based on the Association of Religion Data Archives information from 2000 which was also analyzed by the Church Planting Center at the Southern Baptist Theological Seminary.4 The Center’s report and PowerPoint presentation state that greater Boston is 2.5% evangelical.5 Since the ARDA data fails to include most of the Black Protestant, Hispanic, Haitian, Brazilian, and Asian churches under its evangelical category, it clearly underestimates the evangelical percentage. Even the slightly improved 2010 ARDA data only identifies 7,439 Black Protestants in Greater Boston.6 Just one black church (Jubilee Christian Church) of the city of Boston’s more than 200 black churches has about that number of members. In Greater Boston, there are many more black churches not counted in this study. If the city of Boston has about 100 largely uncounted evangelical Spanish-speaking churches, then Greater Boston (which includes Lawrence, Mass.) has at least double that number. This study also does not account for the many evangelical churches which in urban areas are affiliated with denominations classified by ARDA as “Mainline.” For example, more than 60 American Baptist churches in Greater Boston could be classified as evangelical rather than mainline. Numbers and percentages based on the ARDA data, therefore, fail to identify hundreds of evangelical churches in Greater Boston, and some of these are among the area’s largest churches.
What about the Barna Research Group?
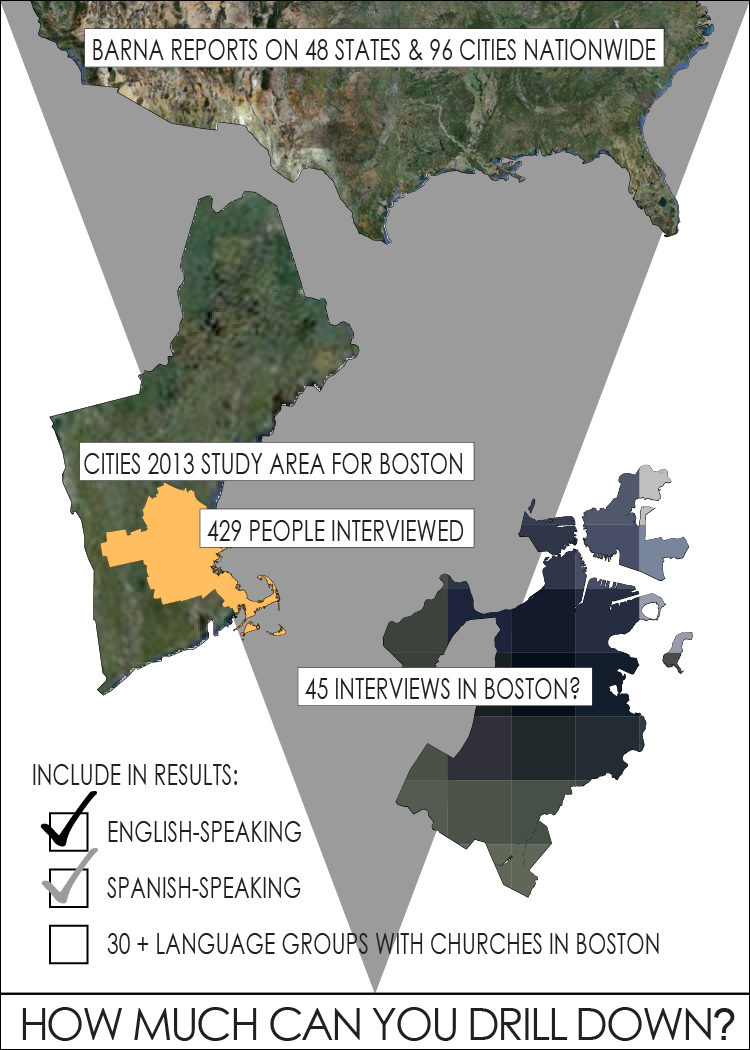
The Barna Research Group has produced many reports on the beliefs and practices of Americans using phone surveys. By drawing on 42,000 interviews completed over the last five to ten years, they have compiled statistics which they have sliced up into 96 cities ("urban media markets”). The most recent of these Barna Reports are called Cities 2013. Barna also has produced parallel reports on 48 states.
The Cities 2013 report for the Boston area might give the impression to many people that it gives data primarily on the city of Boston or the city and its immediate suburbs. It is important to realize that this report covers an area extending from Nantucket to Laconia, New Hampshire, and eastern Vermont, as well as Worcester County, Massachusetts. The adult population of this media market area (DMA) in 2010 was 4,946,945 while the city of Boston’s adult population was 513,884 or only 10.4% of the total area.7 The total population of Barna’s “Boston” area was 6,322,433 compared to the total Boston city population of 617,594 (9.8% of the area). When using statistics from the Barna Cities 2013 report, one must keep in mind that the city of Boston is only a small part (~10%) of the area covered.
The Boston Cities 2013 Report is based on 429 interviews according to the Barna Research Group. Since the city of Boston represents 10.4% of the area’s adult population, one can estimate that about 45 interviews were done in Boston. Given the diversity of languages, racial groups, and nationalities in the city with its population of over a half-million adults, it is hard to imagine that this sample was large enough and representative enough to give a true picture of religious faith and practice in Boston. In addition, “while some interviews were conducted in Spanish, most were conducted in English. No interviewing was done in languages other than Spanish and English.”8 In fact, the Barna website says, “the vast majority of the interviews were completed in English.”9 Since the city of Boston has over 100,000 (17.5%) Hispanics10 with more than 100 churches, it is quite likely this group is underrepresented. This is just one of over 30 language groups which have churches in Boston. In the larger Barna study area (Boston DMA), there are 522,867 Hispanics and 344,157 Asians.11 The area also includes a very large Brazilian population with over 400 Brazilian churches and the fourth largest population of Haitian Americans with dozens of thriving Haitian churches. Because these language groups were significantly less likely to be included in the interviews, and because many of these groups are among the most active in Christian faith and practice, the Boston area report underestimates Christian beliefs and involvement in the area and especially if one equates its conclusions with the city of Boston.
Table of total populations of the City of Boston and the DMA media market area. (The Boston DMA area is the one used by the Barna Research group.)
What about the Gallup Polls on religion?
The Gallup organization interviews large numbers of adults every year on a variety of topics including religion. Recent reports have not only examined national trends, but have also analyzed how religious the various states and metropolitan areas are. During 2012, Gallup completed more than 348,000 telephone interviews with American adults aged 18 years and over.12 The Gallup organization uses what it calls the Gallup Religiousness Index when it states that one state or city is more religious than another. Specifically it is comparing the percentage of adults in the various states or cities who are classified as “very religious.” Two questions are used in the Gallup Religiousness Index:
(2) “How often do you attend church, synagogue or mosque? – at least once a week, almost every week, about once a month, seldom, never, don’t know, refused.”13
For someone to be classified as “very religious,” he or she would need to answer, “Yes, religion is an important part of my daily life,” and “I attend church, synagogue, or mosque at least once a week or almost every week.”
Nationally, 40% of American adults were found to be “very religious” on the basis of this standard. Significantly more Protestants (51%) were “very religious” than Catholics (43%).14 Religiousness generally increases with age, and so young adults are less religious than seniors.
The Gallup surveys have found that the New England states, including Massachusetts, have lower percentages of adults who are “very religious.” In fact, (1) Vermont (19%), (2) New Hampshire (23%), (3) Maine (24%), (4) Massachusetts (27%), and (5) Rhode Island (29%) are the five least religious states according to this measure.15 Several New England metropolitan areas also ranked low on the religiousness scale (Burlington, VT; Manchester-Nashua, NH; Portland, Maine). The Boston-Cambridge-Quincy metropolitan area ranked eighth least religious, with 25% of its metro area adults classified as “very religious.”16 Although many new churches have started in Boston and there is significant spiritual vitality in the city, two factors probably contribute to the low ranking. Boston has the largest percentage of young adults aged 20 to 34 years old of any major city in the country. This age group has lower percentages of “very religious” people than the older age groups. Also, Boston has a high percentage of Catholics (46.4%), and Catholics have a significantly lower percentage of “very religious” adherents.17 This factor also plays a role in the Massachusetts state ranking, since Massachusetts is now “the most heavily Catholic state in the union” (44.9%).18 One must keep in mind that the Gallup Religiousness Index is just one way of measuring how religious a person is, and it is based on self-reporting. The question about the importance of religion in one’s daily life can have many different meanings to different people. Other research has shown that the frequency of church attendance “does not predict or drive spiritual growth” for all groups of people.19
Some Quick Advice for Boston Church Statistic Users
From these examples, you can see that it is important to evaluate critically the religious statistics you read in the media. In some cases these statistics may be incomplete, inaccurate, or have large margins of error. In looking at the data for a city, you also need to understand the geographic area the report is studying. This could range from the named city’s official city limits, to its county, metropolitan statistical area, or even to a media area covering several surrounding states. In reading religious statistics and comparisons, you also need to carefully understand definitions and categories that the research uses. A study may categorize and count Black churches or Evangelical churches in ways that fail to count many of those churches. When a survey says one state is more religious than another, you need to understand how the study defines “religious.” Using religious research statistics without careful evaluation and study can lead to misinterpretation and spreading misinformation.
_______________
1 To accurately compare numbers, we compare only Christian churches from both our count and the U.S. Religious Census (which also included other religious groups such as Buddhists, etc.).
2 “Appendix C / African American Church Bodies,” 2010 U. S. Religion Census: Religious Congregations & Membership Study, 675, www.USReligionCensus.org (accessed 28 March 2013).
3 Cairo Marques and Josimar Salum, “The Church among Brazilians in New England,” in New England’s Book of Acts, edited by Rudy Mitchell and Brian Corcoran (Boston: Emmanuel Gospel Center, 2007), II:15. See link here.
4 J. D. Payne, Renee Emerson, and Matthew Pierce, “From 35,000 to 15,000 Feet: Evangelicals in the United States and Canada,” Church Planting Center, Southern Baptist Theological Center, 2010.
5 Ibid.
6 Association of Religion Data Archives, “Boston-Cambridge-Newton, MA, NH Metropolitan Statistical Area: Religious Traditions 2010,” www.thearda.com (accessed 5 May 2013).
7 U.S. Census 2010, Summary File 1, Table DP1 (Population 18 and over). The Barna interviews were only with adults.
8 Pam Jacob, “Barna Research Group,” Email. 2 April 2013.
9 Barna Research Group, “Survey Methodology: The Research Behind Cities,” Barna: Cities. Barna Cities & States Reports (accessed 8 April 2013).
10 U.S. Census 2010, Summary File 1, Table DP1.
11 U. S. Census 2010, Summary File 1, Table DP1.
12Frank Newport, “Mississippi Maintains Hold as Most Religious U.S. State,” Gallup, 13 Feb. 2013 www.gallup.com (accessed 24 April 2013).
13 Ibid.
14 Ibid.
15 Ibid.
16 Ibid.
17 Catholic Hierarchy website, Boston Archdiocese, 2006, www.catholic-hierarchy.org/diocese/dbost (accessed 24 April 2013).
18 “Massachusetts Now Most Catholic State,” Pilot Catholic News, 11 May 2012, www.PilotCatholicNews.com (accessed 24 April 2012)
19 Greg L. Hawkins and Cally Parkinson, Move: What 1,000 Churches Reveal About Spiritual Growth (Grand Rapids, Mich.: Zondervan, 2011), 18-19.










![Ethiopian Churches in Greater Boston [map]](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/57ff1c7ae58c62d6f84ba841/1506113852983-TSLLC1FENTJJGZYIO7MM/orthodox+cross+church.jpeg)


